Stemmy
THE CELL
We're the Foundation of Development
© Stemmy 2020. All rights reserved.
WHAT ARE STEM CELLS?
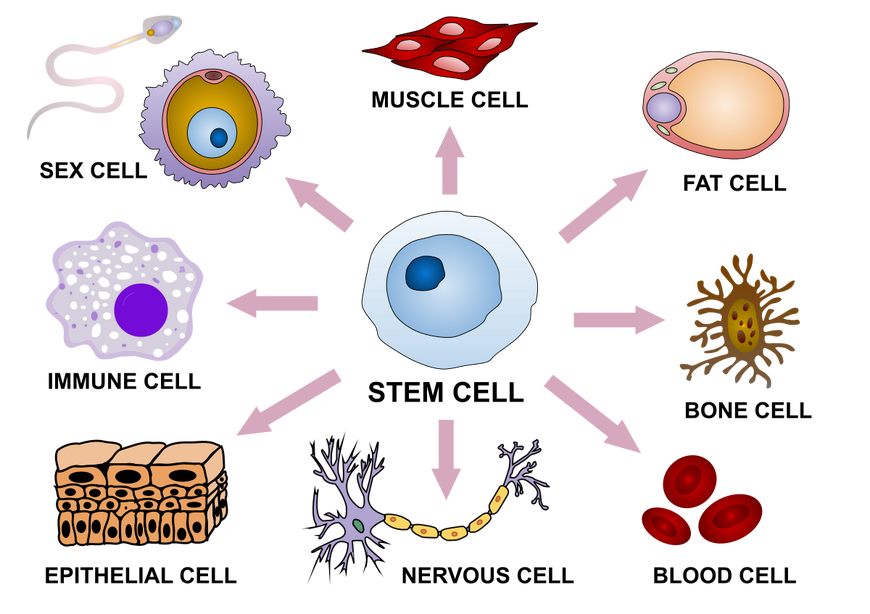
Stem cells are the foundation of development in plants, animals and humans. They are self-renewing, unspecialized cells that can give rise to multiple cell types of all tissues of the bodies. All stem cells can replicate many times for long periods, differentiate to develop specialized cells in the body and regenerate to replace damaged cells.
A stem cell can become any one of the 220 different cells in the body. At the start of life, stem cells divide over and over again to create a full person from an embryo. As we age, they replenish cells in our blood, bone, skin and organs. This is important because they could be powerful tools in treating injury and illness.
| Type of Stem Cells | Function | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| TOTIPOTENT | The most powerful that exist and can generate a fully-functional, living organism. It can differentiate into embryonic, as well as extra-embryonic tissues, such as chorion, yolk sac, amnion, and the allantois. In humans and other placental animals, these tissues form the placenta. | Fertilized egg that is formed when a sperm and egg unite to form a zygote, specifically cells of embryo of 1-3 days. |
| PLURIPOTENT | It can self-renew and differentiate into any of the three germ layers: endoderm, ectoderm & mesoderm. Because of their powerful ability to differentiate in a wide diversity of tissues and their non-controversial nature, induced pluripotent stem cells, a tissue-specific cells, are well-suited for use in cellular therapy and regenerative medicine. | Embryonic stem cells, which exist in an early-stage embryo, and Induced Pluripotent stem cells that can be reprogrammed to become functionally similar to embryonic stem cells. |
| MULTIPOTENT | Middle-range type of stem cell, in that they can self-renew and differentiate into a specific range of cell types. These cells types are fairly diverse in their characteristics | Mesenchymal stem cells can differentiate into osteoblasts, myocytes, adipocytes, & chondrocytes. |
| OLIGOPOTENT | Similar to the multipotent stem cells, but they become further restricted in their capacity to differentiate. It can only do so into closely related cell types, such as lymphoid or myeloid stem cells. | Hematopoietic stem cell from the mesoderm that can differentiate into blood cells. Corneal epithelium, a squamous epithelium that is constantly renewing. |
| UNIPOTENT | The least potent and most limited type of stem cell. It can produce only one cell type, their own, but have the property of self-renewal, which distinguishes them from non-stem cells. | Muscle stem cells can only do so into a single cell type. They are unidirectional in their differentiation capacity. |
STEM CELL THERAPY
Stem-cell in the area of research mainly studies the properties of stem cells and their potential use in medicine. As stem cells are the source of all tissues, understanding their properties helps in our understanding of the healthy and diseased body's development and homeostasis.
• Process of Cell Differentiation
A primary goal of research on embryonic stem cells is to learn how undifferentiated stem cells turn into differentiated stem cells that form specific tissues and organs. Researchers are also interested in figuring out how to control this process of differentiation.
Over the years, scientists have developed methods to manipulate the stem cell process to create a particular cell type. This process is called directed differentiation. A recent study also discovered the first steps in how stem cells transform into brain cells and other types of cells. More research on this topic is ongoing.
• Cell-based Therapies
If researchers can find a reliable way to direct the differentiation of embryonic stem cells, they may be able to use the cells to treat certain diseases. For example, by directing the embryonic stem cells to turn into insulin-producing cells, they may be able to transplant the cells into people with type 1 diabetes.
• Stem Cells to Test New Drugs
Researchers are also using differentiated stem cells to test the safety and effectiveness of new medications. Testing drugs on human stem cells eliminates the need to test them on animals.















